
What is TDD?

- TDD is based on two rules:
- Do not write code unless there is a test failing.
- Eliminates duplicates (DRY).
- The mantra used in TDD is:
- RED.
- GREEN.
- REFACTOR.
- TDD has two types of tests:
- Unit test.
- Acceptance test.
FDD (Feature Driven Development)
Each characteristic is related to a small value feature.
Roles:
- Project Director.
- Chief Architect.
- Development Director.
- Chief Programmer.
- Owner of the class and/or domain expert.
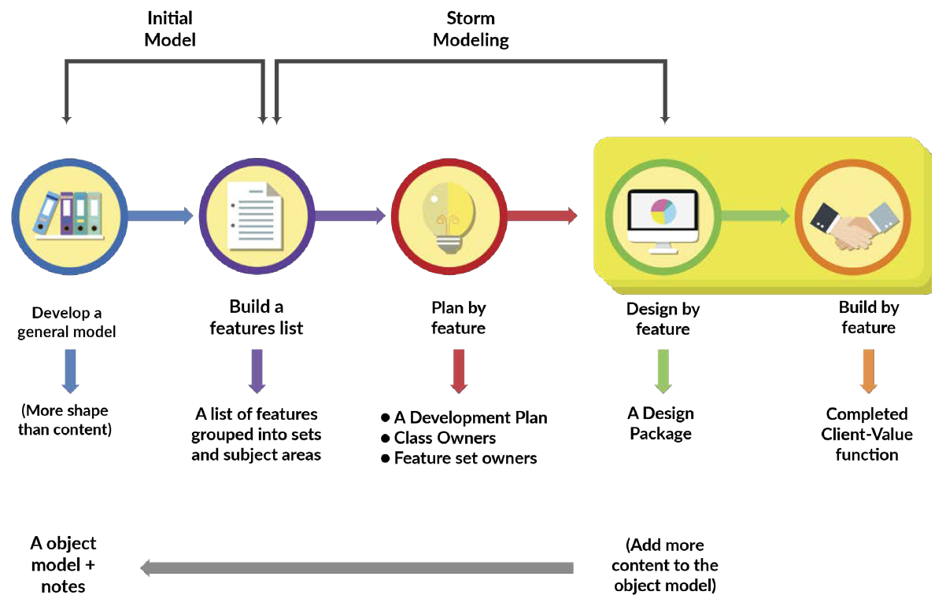
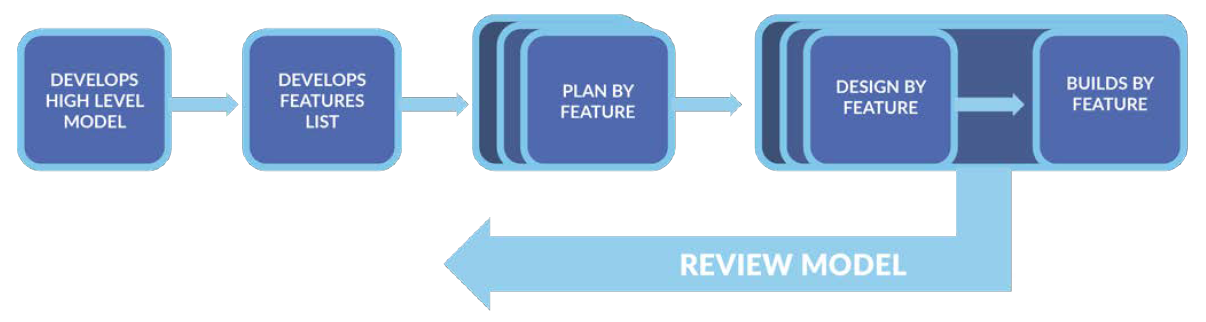
Organized in 5 stages that progress iteratively:Develop a general high-level model.
- Build a list of features.
- Plan by features.
- Design by feature.
- Build by feature.
Uses best software development practices such as:
- Subject objects based model.
- Development by features.
- Individual class property.
- Teams by features.
- Inspections.
- Configuration management.
- Periodic construction.
- Visibility of the process and results.
Crystal Methodologies

Benefits:
-
They are appropriate for light environments.
- Cost reduction is experienced since they are designed for change.
- Present more transparent planning for customers.
- In each iteration, the objectives for the following iteration are defined.
- Allow very useful feedback from the users.
Challenges:
- Delimits the scope of the project with the client.
- It may not be feasible for large projects.
- Stablishes assigned teams but not the distribution.
- Still under development.
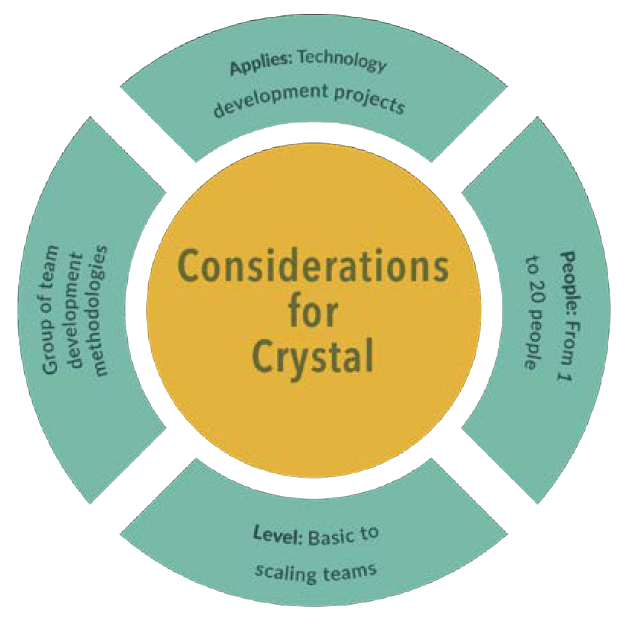
Introduction to Crystal Methodologies

- Group of methodologies introduced by Alistair Cockburn in the early 90s.
-
Based on the observation of several teams that followed Agile methodologies.
- People-focused.
- The development process and tools are not fixed.
- Adjusted to the requirements and specific characteristics of the project.
- They are “light methodologies” that avoid strict processes.
The name comes from precious stones. Factors such as:
- Comfort.
- Money at discretion.
- Essential money.
- Life.

Última modificación: miércoles, 6 de abril de 2022, 15:47